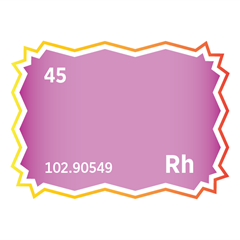
Ontario
Critical minerals, policy, and the energy transition
The Energy Transition in Ontario, Canada
Ontario, the economic powerhouse of Canada, stands at the forefront of a transformative energy transition. With its vibrant cities, expansive landscapes, and diverse industries, the province is spearheading innovative initiatives to embrace sustainability and resilience in its energy sector. A strategic blend of renewable energy integration, technological innovation, and policy leadership defines Ontario's energy transition. The province has set ambitious targets to reduce carbon emissions, increase renewable energy generation, and promote energy efficiency, positioning itself as a trailblazer in Canada's quest for a cleaner and greener future. Leveraging its abundant natural resources and advanced infrastructure, Ontario is diversifying its energy mix to include wind, solar, hydroelectric, and nuclear power. The province's commitment to renewable energy is evident through its significant investments in wind farms and solar installations. The province is home to a thriving clean technology industry, with research institutions, startups, and established companies working together to develop cutting-edge solutions for energy efficiency, grid modernization, and carbon reduction.
Ontario's energy revolution
Ontario is embarking on a comprehensive energy revolution, driven by the need to meet growing electricity demand, reduce emissions, and maintain economic competitiveness. It is characterised by a diverse mix of nuclear, renewable, and natural gas projects, supported by significant investments in infrastructure and energy efficiency. The province’s strategy focuses on an all-of-the-above approach, integrating nuclear, renewable, and natural gas energy sources while expanding infrastructure and investing in energy efficiency.
Nuclear energy expansion
Nuclear power remains a cornerstone of Ontario’s energy strategy. The province is advancing projects like the refurbishment of the Pickering Nuclear Generating Station, which will produce over 2,000 megawatts of electricity, enough to power two million homes. Additionally, small modular reactors (SMRs) at the Darlington site are being developed, with the first unit expected to be operational by 2028. These initiatives aim to provide reliable, zero-emission energy while supporting Ontario’s goal of becoming a global energy superpower.
Renewable energy and storage
Ontario is also expanding its renewable energy capacity. The Second Long-Term Procurement (LT2) program, launched in December 2024, targets up to 7,500 megawatts of new electricity generation from wind, solar, and energy storage projects between 2025 and 2028. This represents a significant opportunity for the renewable energy sector, which has not seen new procurement in nearly a decade. Additionally, the Oneida Energy Storage Project, an Indigenous-led initiative, will add 250 megawatts of battery storage, enhancing grid reliability and reducing emissions.
Natural gas and electrification
While renewables and nuclear are prioritized, natural gas continues to play a role in ensuring grid reliability. The province has introduced policies allowing natural gas plants to operate until 2035, providing a bridge to a cleaner grid. However, this approach has drawn criticism for potentially undermining emissions reduction goals. Ontario is also investing in electrification, including the development of electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure and industrial electrification projects, such as the conversion of Algoma Steel to electric arc furnaces.
Energy efficiency and consumer programs
To manage rising demand, Ontario has launched a $10.9 billion energy efficiency initiative, offering rebates for home retrofits, including insulation, heat pumps, and solar panels. This program aims to reduce peak electricity demand by 3,000 megawatts by 2036, equivalent to taking three million homes off the grid. The Market Renewal Program (MRP), set to launch in 2025, will improve electricity market transparency and predictability, helping businesses navigate the energy transition.
Federal and provincial collaboration
The federal government has supported Ontario’s energy transition through investments in nuclear, renewables, and energy storage. For example, $50 million was allocated for Bruce Power’s assessment of new nuclear generation opportunities, and $970 million was invested in SMR development at Darlington.
Economic and environmental benefits
Ontario’s energy strategy is expected to attract billions in investment, create jobs, and reduce emissions. The province’s grid is already 92% clean, and initiatives like the Clean Electricity Regulations (CER) aim to achieve a net-zero grid by 2035. However, challenges remain, including balancing natural gas use with long-term climate goals and ensuring affordability for consumers.


Source: SFA (Oxford)
Energy Raw Materials and products produced in Ontario
Essential minerals production and products in Ontario
The journey of Canada's critical minerals
Canada's renewable energy progress hinges on crucial minerals like lithium, nickel and cobalt, PGMs, rare earths, and minor metals, essential for low carbon and future technologies supported by sustainable mining and innovation policies. This strategy underscores the importance of these minerals in achieving a future of sustainability and energy security. Discover how these critical minerals are pivotal to Canada's sustainable energy transition.

Meet the Critical Minerals team
Trusted advice from a dedicated team of experts.

Henk de Hoop
Chief Executive Officer

Beresford Clarke
Managing Director: Technical & Research

Jamie Underwood
Principal Consultant

Ismet Soyocak
ESG & Critical Minerals Lead

Rj Coetzee
Senior Market Analyst: Battery Materials and Technologies

How can we help you?
SFA (Oxford) provides bespoke, independent intelligence on the strategic metal markets, specifically tailored to your needs. To find out more about what we can offer you, please contact us.