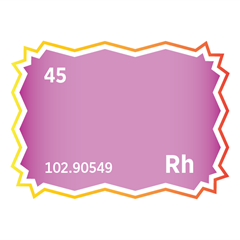
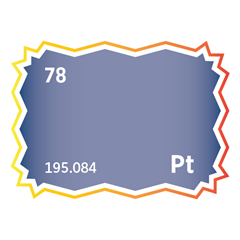
Canada
Critical minerals, policy, and the energy transition
The Energy Transition in Canada
Colombia’s pursuit of an energy transition reflects its growing alignment with global climate objectives and its aspiration to modernise its economy through more sustainable and diversified energy systems. As a resource-rich nation with a long history of extractive industries, Colombia is now seeking to pivot from traditional hydrocarbon dependence towards cleaner energy sources such as solar and hydropower, while also positioning itself as a future supplier of critical minerals vital to global decarbonisation efforts. The country holds a varied portfolio of strategic resources, including copper, nickel, platinum, and barium—minerals increasingly in demand for renewable energy infrastructure, electric vehicles, and advanced manufacturing. Yet Colombia’s energy transition is shaped as much by political geography as by geology. Its decentralised governance structures layered environmental regulations, and the need to navigate Indigenous and Afro-Colombian land rights introduce significant legal and operational complexity. Moreover, the country’s mineral-rich regions are often characterised by social conflict, illicit economies, and fragile institutions, complicating efforts to build secure and transparent supply chains. Colombia’s engagement with international frameworks such as the OECD, IADB, and G77 highlights its desire to integrate into responsible global markets but also reveals the tension between attracting foreign investment and asserting national sovereignty over its natural resources. In this evolving context, Colombia’s energy transition is not only a technical or economic challenge, it is a geopolitical balancing act between development, governance, and global demand.
Latest news and insights
Stay ahead in the energy transition with SFA (Oxford)’s cutting-edge insights into how critical minerals, geopolitics, ESG, and supply chain risks are reshaping global growth and redefining Canada's strategic priorities.

Bridging the cobalt gap in the North American market
4 March 2024 | Kimberly Berman
EVelution is at the forefront of the EV revolution in North America and is breaking ground on a $200 million project that will produce up 33,000 metric tons of cobalt sulfate annually.

Can Canada become an EV powerhouse?
18 February 2024 | Kimberly Berman
With an abundance of critical raw materials, a robust automotive industry, and strong government support, there is an urgent need for Canada to develop its own midstream supply chain to support the EV industry.
Canada's international economic, trade, and security alliances
A comprehensive approach to the global energy transition
Canada is positioning itself at the forefront of the global energy transition through the adoption of renewable energy, critical mineral development, technological innovation, and robust policy frameworks.
Canada’s approach to critical minerals and the energy transition is deeply intertwined with its international alliances. These relationships enable Canada to influence global policies, secure essential resources, and collaborate on innovative solutions for a sustainable future. The federal and provincial governments are implementing robust policy frameworks to support the energy transition. The Pan-Canadian Framework on Clean Growth and Climate Change outlines the national strategy for reducing emissions, fostering clean technology, and creating resilient communities. Carbon pricing mechanisms, renewable energy incentives, and emissions regulations are key components of this framework.
The energy transition in Canada faces several challenges to becoming a global leader in clean energy. Infrastructure development is essential, requiring the upgrade of the national grid to accommodate renewable energy sources. Regulatory hurdles present another obstacle, as the country must navigate complex and varied regulatory environments across its provinces. Economic diversification is also critical, as Canada needs to balance economic growth while shifting away from fossil fuels. Additionally, social acceptance is a crucial factor, necessitating efforts to ensure community support for renewable energy projects. These challenges must be met with innovative solutions and collaborative efforts to achieve a sustainable energy future.


Source: SFA (Oxford)
Critical Minerals mapping and policy developments
Provincial efforts to develop and manage critical minerals in Canada are diverse and tailored to local contexts, with each key province contributing uniquely to the energy transition. Quebec, a leader in hydropower, is emerging as a significant player in lithium production. Ontario focuses on integrating nuclear power and renewable energy while playing a vital role in nickel and cobalt production. British Columbia is developing hydro, wind, and solar power and boasts significant deposits of copper, nickel, and other critical minerals. Alberta is transitioning from oil sands to renewable energy sources like wind and solar and leads in lithium extraction practices. Saskatchewan invests in wind power, explores small modular nuclear reactors (SMRs), and focuses on uranium and other critical minerals.
In Newfoundland and Labrador, significant advancements have been made in nickel and cobalt development, while Manitoba is developing strategies for these minerals. The Northwest Territories are mapping rare earth elements and other critical minerals, and Nunavut is actively exploring and developing critical minerals. Yukon explores rare earth elements and sustainable mining practices. New Brunswick and Prince Edward Island are exploring the potential for rare earth elements, and Nova Scotia emphasises sustainable mining practices.
Each province's unique approach reflects the regional strengths and resources available, contributing collectively to Canada's overall strategy in critical minerals and the energy transition. Discover the energy transition and critical minerals across Canada.
Canada's energy and power mix
Critical Minerals in Canada
Energy Raw Materials and products produced in Canada
Essential Mineral Production and Products in Canada



Meet the Critical Minerals team
Trusted advice from a dedicated team of experts.

Henk de Hoop
Chief Executive Officer

Beresford Clarke
Managing Director: Technical & Research

Jamie Underwood
Principal Consultant

Ismet Soyocak
ESG & Critical Minerals Lead

Rj Coetzee
Senior Market Analyst: Battery Materials and Technologies

How can we help you?
SFA (Oxford) provides bespoke, independent intelligence on the strategic metal markets, specifically tailored to your needs. To find out more about what we can offer you, please contact us.