Servers and Data Storage Centres
Critical minerals, policy, and the energy transition
Critical Minerals and Servers and Data Storage
The modern digital economy relies on vast networks of servers and data storage systems to support cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and global communications. At the heart of these technologies are critical minerals, which provide the structural strength, electrical conductivity, thermal management, and data processing capabilities necessary for high-performance computing. These minerals are essential in semiconductor fabrication, circuit board manufacturing, data storage technologies, and power management systems, ensuring the efficiency, durability, and reliability of modern data centres. From structural and conductive metals that form the physical framework of servers to precious and semiconductor-grade materials that power data processing and storage, each mineral plays a distinct and vital role. Their applications range from high-speed processors and fibre-optic communication to soldering materials that ensure long-lasting circuit connections. As the demand for faster computing, greater energy efficiency, and expanded data storage capacity continues to grow, the availability and responsible sourcing of these critical minerals will be fundamental to sustaining and advancing digital infrastructure. The following sections highlight key minerals in servers and data storage and their roles in ensuring high-speed, reliable, and efficient computing.
Key Minerals and their Roles
Structural and conductive metals in servers and data storage
Servers and data storage systems rely on a combination of strong, durable materials for physical support and highly conductive metals for efficient power distribution and heat dissipation. These metals play a crucial role in ensuring the reliability, longevity, and thermal stability of critical server infrastructure, contributing to structural integrity, conductivity, and effective heat management. This, in turn, helps maintain stable performance in high-density computing environments.
-
Aluminium is widely used in server chassis, heat sinks, and cooling solutions due to its lightweight nature, high thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion. Its ability to efficiently dissipate heat is crucial in preventing the overheating of processors and memory modules. Additionally, aluminium alloys are often used in data centre infrastructure for their strength-to-weight ratio, helping to reduce overall system weight while maintaining durability.
-
Copper plays a vital role in power distribution systems, server motherboards, and high-performance cooling solutions. Due to its exceptional electrical and thermal conductivity, copper is essential for printed circuit boards (PCBs), which connect and transfer data between server components. It is also used in liquid cooling systems, heat pipes, and thermal interface materials (TIMs) to improve energy efficiency and reduce heat build-up in high-density server environments.
-
Iron is primarily used in server rack structures, chassis reinforcements, and electromagnetic shielding. As a fundamental element in steel alloys, it provides strength and durability to server enclosures and mounting systems. Additionally, iron-containing materials help shield electronic components from electromagnetic interference (EMI), reducing signal disruptions in densely packed data centre environments.
-
Nickel is a key component in server cooling systems, particularly in superalloys used for high-performance heat exchangers and thermal management solutions. Its corrosion resistance ensures long-term reliability in harsh operating conditions. Nickel is also used in electroplating server components to enhance durability and prevent oxidation, especially in connectors and high-frequency transmission systems.
-
Zinc is commonly used for galvanisation, a process that coats steel components to prevent rust and corrosion. In data centres, zinc-coated (galvanised) server racks and enclosures help extend the lifespan of infrastructure, especially in high-humidity environments. Zinc alloys are also used in die-cast components for structural stability and shielding applications.
Magnetic and data storage materials
Servers and data storage systems rely on highly specialised magnetic materials to enable efficient data storage and retrieval. These elements are essential for hard disk drives (HDDs), solid-state drives (SSDs), and other magnetic storage technologies, contributing to high-speed performance, data integrity, and overall system efficiency. They play a crucial role in magnets, shielding, and soldering materials, enhancing the durability and reliability of modern data storage infrastructure. By integrating these advanced materials, servers and data centres can achieve faster, more efficient, and more resilient storage solutions, meeting the ever-growing demand for high-speed data processing and secure digital infrastructure.
-
Barium is widely used in ferrite magnets, which are essential for data storage applications and shielding against electromagnetic interference (EMI). By reducing signal disruptions, barium helps improve the stability and reliability of data transmission within servers and storage devices.
-
Praseodymium plays a key role in rare-earth magnets, particularly in HDD actuators and optical components within data storage systems. Its unique properties contribute to high-performance read/write mechanisms, allowing for faster and more accurate data access.
-
Neodymium is a critical component in neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets, which are integral to HDD actuators and spindle motors. These magnets provide the necessary precision and force for rapid data retrieval, making them indispensable in high-speed storage solutions.
-
Bismuth is commonly applied in low-melting alloys and soldering materials used in HDDs and circuit boards. Its non-toxic and lead-free properties make it a valuable alternative in environmentally friendly server and storage hardware manufacturing.
-
Dysprosium enhances the heat resistance and magnetic stability of neodymium-based magnets, ensuring they maintain strong magnetic properties even under high temperatures. This is particularly important in HDDs and data centres, where sustained high performance and thermal resilience are required.
Precious metals for electrical contacts and circuitry
Servers and data storage systems rely on precious metals for their high reliability, corrosion resistance, and electrical efficiency. These elements play a critical role in connectors, circuit board contacts, capacitors, and magnetic storage coatings, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in high-speed computing environments. Their ability to maintain stable electrical conductivity under demanding conditions makes them indispensable in data centres and advanced semiconductor technologies.
-
Ruthenium is applied in advanced magnetic storage coatings for HDDs, where it enhances durability, wear resistance, and overall drive performance, extending the lifespan of high-density storage solutions.
-
Palladium is a key material in multilayer ceramic capacitors (MLCCs), which are essential for regulating power and ensuring signal stability in data centre electronics and server motherboards.
-
Silver is found in high-performance connectors and soldering materials, where its exceptional electrical conductivity enhances signal integrity and power efficiency in server and data storage hardware.
-
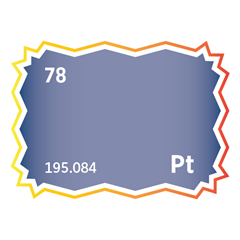
Platinum is used in hard drive coatings, high-end semiconductor manufacturing, and catalytic converters in power supply units. Its high resistance to wear and chemical degradation makes it ideal for long-lasting, high-performance components.
-
Gold is widely used in electrical connectors, circuit board contacts, and high-speed data transmission due to its excellent conductivity and resistance to oxidation. Its superior reliability makes it essential for high-performance server components.
Semiconductor and chip manufacturing elements
Semiconductors form the backbone of modern computing, powering processors, memory chips, and high-speed data transmission systems. The elements used in semiconductor fabrication are essential for boosting processing power, increasing efficiency, and enabling miniaturisation in advanced computing technologies. These materials play a crucial role in thermal management, high-speed electronics, and fibre-optic communication, ensuring the seamless operation of servers, data centres, and digital infrastructure. By incorporating these specialised elements, servers and data centres can achieve faster processing speeds, greater energy efficiency, and enhanced data transmission, paving the way for high-performance computing and AI-driven innovation.
-
Beryllium is used in thermal management solutions and high-performance electronic components, where its high thermal conductivity and mechanical strength help dissipate heat in processors and semiconductor devices.
-
Silicon is the fundamental element in all semiconductor chips, forming the basis of CPUs, GPUs, and memory storage. Its excellent semiconducting properties make it indispensable in data processing and storage technologies.
-
Gallium is a crucial material for gallium nitride (GaN) and gallium arsenide (GaAs) semiconductors, which are widely used in high-speed processors and advanced telecommunications equipment due to their high electron mobility and efficiency.
-
Germanium is used in fibre optics and semiconductor components, improving high-speed data transmission and optical communication, both of which are critical for data centres and cloud computing infrastructure.
-
Arsenic is a key element in gallium arsenide (GaAs) semiconductors, which enable high-speed data processing and efficient power conversion in advanced computing and telecommunications technologies.
-
Hafnium is found in high-k dielectric materials, which are essential for modern semiconductor chips. These materials allow for greater transistor density and lower power consumption in cutting-edge processors and memory devices.
Soldering, circuitry, and anti-corrosion materials
Servers and data storage systems rely on specialised materials to ensure circuit board reliability, thermal stability, and long-term durability. These elements play a crucial role in soldering, corrosion resistance, and electronic protection, helping to maintain the structural integrity and efficiency of server hardware. By enhancing conductivity, thermal management, and fire resistance, these materials contribute to the longevity and reliability of modern data centres and computing infrastructure.
-
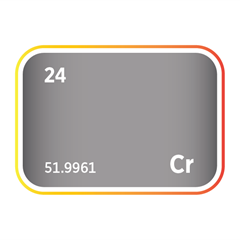
Chromium is widely used in stainless steel components and protective coatings, providing corrosion resistance and durability to server enclosures, heat sinks, and infrastructure.
-
Manganese is essential in battery storage systems and alloying metals used in server construction, where it improves mechanical strength and energy storage capabilities.
-
Tin is a key element in soldering materials, ensuring strong, reliable connections in circuit boards and server components. Its low melting point and excellent conductivity make it indispensable in modern electronics manufacturing.
-
Antimony is commonly used in flame retardants and semiconductor alloys, enhancing fire resistance and thermal stability in circuit boards and electronic components.
-
Tantalum is used in high-reliability capacitors on circuit boards, where its stability under high temperatures and resistance to corrosion help ensure consistent power delivery and long-term performance in data centre servers and advanced computing systems.


Critical sectors using strategic minerals

Meet the Critical Minerals team
Trusted advice from a dedicated team of experts.

Henk de Hoop
Chief Executive Officer

Beresford Clarke
Managing Director: Technical & Research

Jamie Underwood
Principal Consultant

Ismet Soyocak
ESG & Critical Minerals Lead

Rj Coetzee
Senior Market Analyst: Battery Materials and Technologies

How can we help you?
SFA (Oxford) provides bespoke, independent intelligence on the strategic metal markets, specifically tailored to your needs. To find out more about what we can offer you, please contact us.